Genome-wide expression gradient estimation based on local pseudotime in single cell RNA sequencing
Genome-wide expression gradient estimation based on local pseudotime in single cell RNA sequencing
Tjaernberg, A.; Jackson, C.; Bonneau, R.; Christiaen, L.
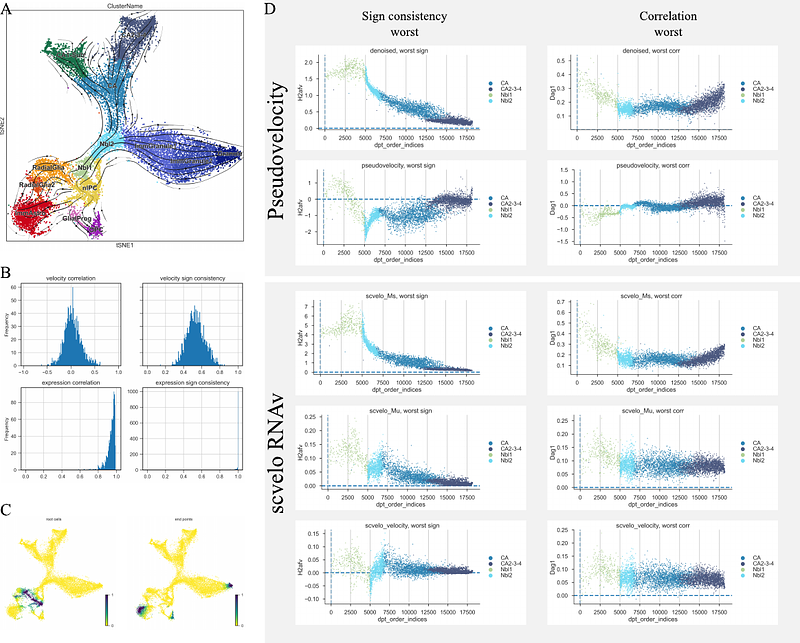
AbstractSingle cell genomics measures the internal state of individual cells and makes it possible to describe biological phenomena such as cell type heterogeneity, developmental progression, and dynamic differentiation using computational methods. A prominent approach to facilitate downstream analysis, for large collection of cells, is to connect individual cells by a k-Nearest Neighbor Graph (kNN-G). The kNN-G is among other things used by methods that derive pseudotime, a temporal ordering of cells. However, pseudotime methods require knowledge of initial states of the trajectories created. Alternatives have been invented that estimate gene rate of transcription e.g. by RNA velocity but these methods don\'t generalize to all individual genes for estimating transcriptional rate of change along pseudotime. While these methods can derive pseudo progression de novo by extrapolating transcription velocity vectors they are limited to subsets of genes where intronic reads are captured with sufficient magnitude. Here we present pseudovelocity, an alternative method for calculating a local rate of change in transcription based on the kNN-G and diffusion-based pseudotime, to derive RNA velocity estimates for individual genes, and demonstrate how it improves the gene-based estimation of RNA velocity for downstream analysis. This package can be accessed here: https://gitlab.com/Xparx/pseudovelocity.