MIST-Explorer: The Comprehensive Toolkit for Spatial Omic Analysis and Visualization of Single-Cell MIST Array Data
MIST-Explorer: The Comprehensive Toolkit for Spatial Omic Analysis and Visualization of Single-Cell MIST Array Data
Fischer, C.; Chen, J.; Meah, A.; Wang, J.
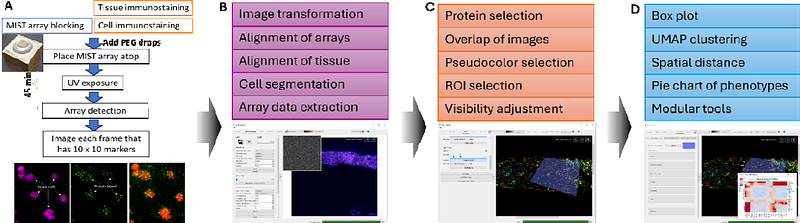
AbstractRecent advances in spatial proteomics have enabled high-dimensional protein analysis within tissue samples, yet few methods accurately detect low-abundance functional proteins. Spatial MIST (Multiplex In Situ Tagging) is one such technique, capable of profiling over 100 protein markers spatially at single-cell resolution on tissue sections and cultured cells. However, despite the availability of various open-source tools for image registration and visualization, no dedicated software exists to align the images and analyze spatial MIST data effectively. To address this gap, we present MIST-Explorer, a comprehensive, user-friendly toolkit for the visualization and analysis of single-cell spatial MIST array data. Developed in Python with a PyQt6-based graphical interface, MIST-Explorer streamlines the spatial omics workflow-from image preprocessing and registration to cell segmentation and protein quantification. The software supports two workflows: one for preprocessed datasets and another for raw image inputs, ensuring broad compatibility across experimental designs. Key features include tile-based image registration using Astroalign and PyStackReg, deep learning-based segmentation with StarDist, multi-channel visualization with layer controls, and an interactive analysis module offering ROI selection along with histograms, heatmaps, and UMAP plots. MIST-Explorer generates spatially resolved expression tables readily compatible with downstream single-cell analysis pipelines. By integrating all major steps into a single platform, MIST-Explorer empowers researchers to derive biological insights from complex spatial omics datasets without requiring extensive computational expertise.