Understanding the physical processes behind DNA-DNA proximity ligation assays
Understanding the physical processes behind DNA-DNA proximity ligation assays
Zubillaga Herrera, B. J.; Das, A.; Burack, L. R.; Wang, A.; Di Pierro, M.
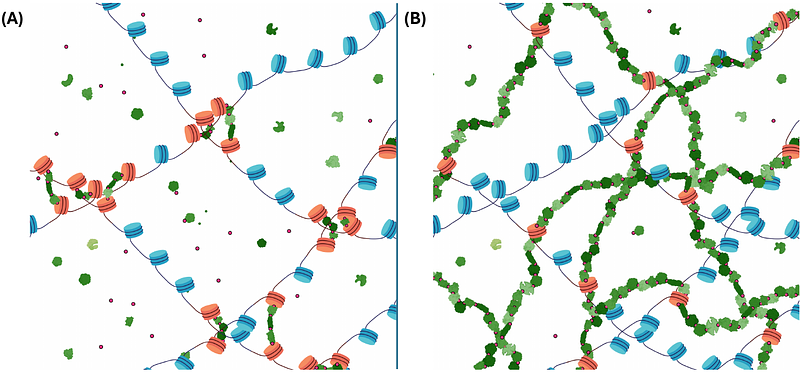
AbstractIn the last decade, DNA-DNA proximity ligation assays opened powerful new ways to study the 3D organization of genomes and have become a mainstay experimental technology. Yet many aspects of these experiments remain poorly understood. We study the inner workings of DNA-DNA proximity ligation assays through numerical experiments and theoretical modeling. Chromosomes are modeled at nucleosome resolution and evolved in time via molecular dynamics. A virtual Hi-C experiment reproduces, in-silico, the different steps of the Hi-C protocol, including: crosslinking of chromatin to an underlying proteic matrix, enzymatic digestion of DNA, and subsequent proximity ligation of DNA open ends. The protocol is simulated on ensembles of different structures as well as individual structures, enabling the construction of ligation maps and the calculation of ligation probabilities as functions of genomic and Euclidean distance. The methods help to assess the effect of the many variables of the Hi-C experiment and of subsequent data processing methods on the quality of the final results.