Safety and immunogenicity of an adjuvanted human onchocerciasis vaccine candidate, OvMANE1: preclinical evaluation in mice model
Safety and immunogenicity of an adjuvanted human onchocerciasis vaccine candidate, OvMANE1: preclinical evaluation in mice model
Nebangwa, D. N.; Efeti, M. T.; Momnougui, S. M. E.; Shintouo, C. M.; Shey, R. A.; Ntie-Kang, F.; Ayiseh, R. B.; Ghogomu, S. M.
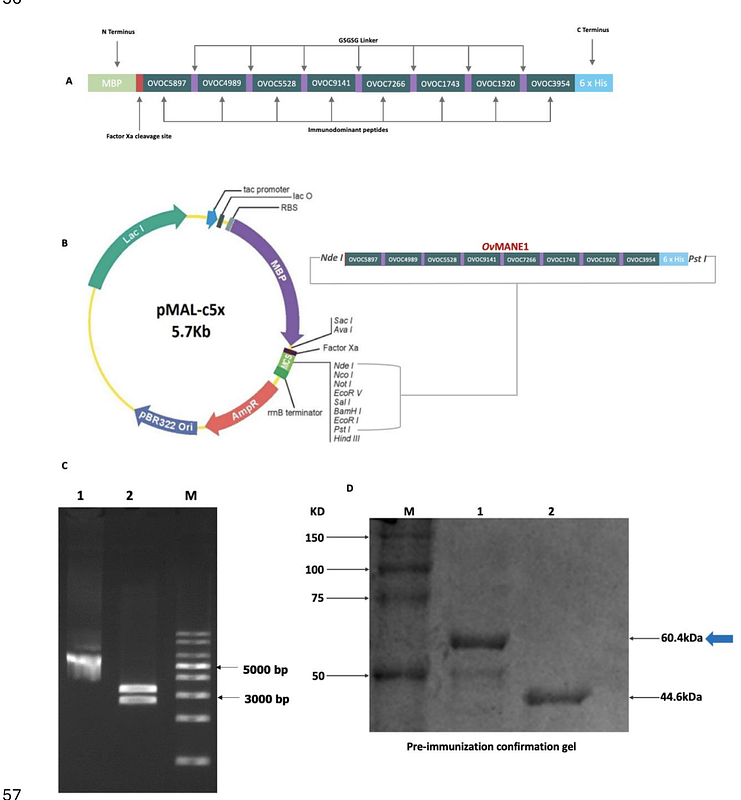
AbstractOnchocerciasis, caused by the filarial worm Onchocerca volvulus, remains a major public health challenge due to the limitations of ivermectin-based control strategies, thereby, highlighting the need for more innovative tools like vaccines. This study investigated the safety and immunogenicity of a novel multi-epitope chimeric antigen, OvMANE1 formulated with Freunds adjuvant, in BALB/c mice. Following mice immunization at three time points of 2-week intervals, adjuvanted-OvMANE1 exhibited a promising safety profile, revealing neither any physical signs of toxicity nor behavioural abnormalities. Immunological assays showed significant increases in total IgG levels after the first (p = 0.0260) and final booster doses (p = 0.026). Interestingly, total IgG (p = 0.0086) and IgG1 (p = 0.0465) levels also increased significantly over the study period highlighting the ability of OvMANE1 to sustain humoral immunity. Moreover, cellular responses were significantly enhanced, with elevated leukocyte count (p = 0.0190) and increased lymphocyte activity (p = 0.0397) observed in the adjuvanted-OvMANE1 group compared to the control. Indeed, total leukocytes increased progressively from day 0 to day 39, with significant differences recorded in the test group between doses: day 0 vs. day 14 (p = 0.0043) and day 14 vs. day 28 (p = 0.0079). The pronounced production of relevant antibodies and induction of cellular immunity strongly suggests that the antigen can elicit mixed Th1/Th2 responses and antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) targeting O. volvulus L3 and/or other larval stages of the parasite. These results clearly show the emergence of OvMANE1 as a promising vaccine candidate against human onchocerciasis. However, further studies to evaluate the antigens protective potential in other animal species are required.