Temperature-Resolved Crystallography Reveals Rigid-Body Dominance Over Local Flexibility in B-Factors
Temperature-Resolved Crystallography Reveals Rigid-Body Dominance Over Local Flexibility in B-Factors
Ribeiro, F. S.; Lima, L. M. T.
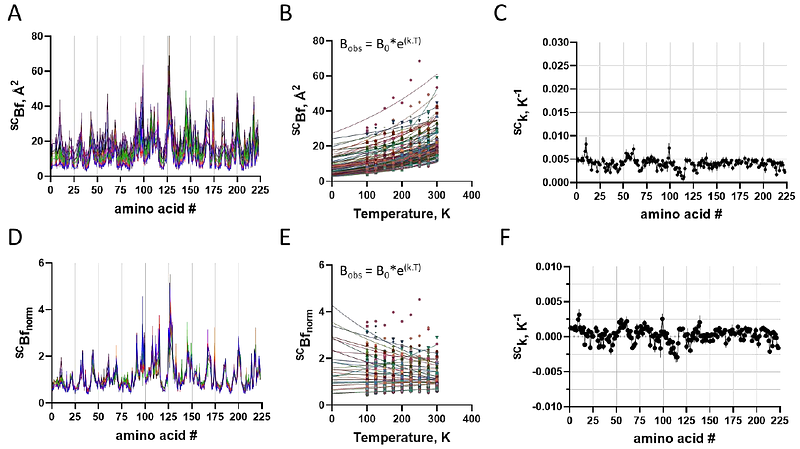
AbstractThe crystallographic B-factor (Bf), also known as the Debye-Waller factor (DWF) or temperature factor, relates to the mean square displacement of atoms (X2). The X2 may be composed of individual contributions from lattice disorder (LT), static conformational heterogeneity (H) throughout the lattice, rigid body vibration (RB), local conformational vibration (V), and zero-point atomic fluctuation (A). The Bf has been widely employed as a surrogate measure of local protein flexibility, although such relation has not been confirmed. In addition, reproducibility of the absolute B-factor is difficult to achieve, hampering the understanding of their individual contribution. Here we report the crystallographic investigation of the enzyme-ligand complex of trypsin with benzamidine from cryo to room temperature, through a 200 K range (9-point triplicate design), by crystal stabilization with hydrophobic grease enabling data collection beyond the protein glass transition (~200 K). The extent of temperature-induced conformational changes showed no connection with their respective B-factors. The B-factor variation due to temperature was constant for all atoms of the system, of about 0.005 K-1. The results caution against interpreting absolute, normalized or zero-point B-factors as direct proxies for protein dynamics, which is further supported by structural analysis of data from independent groups with trypsin-benzamidine complexes obtained under dissimilar experimental conditions. The similar thermal dependence of B-factor for all atoms of the system suggests a major contribution of this physical variable over uniform rigid body vibration.