Sustainable Edamame Production in an Artificial Light Plant Factory with Improved Yield and Quality
Sustainable Edamame Production in an Artificial Light Plant Factory with Improved Yield and Quality
Takano, T.; Wakabayashi, Y.; Wada, S.; Sano, T.; Kawabata, S.; Yamori, W.
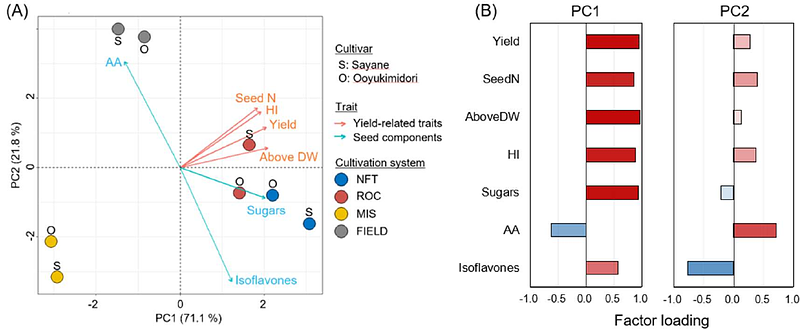
AbstractA plant factory utilizing artificial light is an innovative agricultural model that enables efficient and sustainable crop production. However, its application to a diverse range of crops remains limited. Edamame, a highly nutritious legume, has gained global popularity, yet its long-term storage is challenging due to quality deterioration, restricting its market distribution to seasonal availability. In this study, we successfully cultivated edamame using three hydroponic systems--nutrient film technique (NFT), rockwool, and aeroponics (mist culture)--within an LED plant factory. Among these, NFT demonstrated the highest fresh seed yield, which was comparable to or exceeded that of conventional field cultivation. The high yield was attributed to enhanced pod formation and biomass production under controlled conditions. Furthermore, although free amino acid content was lower in NFT cultivation, NFT-grown edamame exhibited significantly higher total sugar and isoflavone contents than field-grown counterparts, suggesting superior eating quality and nutritional benefits. These results indicate that NFT hydroponics is a promising method for stable, high-yield edamame production with enhanced nutritional properties. This study provides a foundation for expanding edamame cultivation in controlled environments, contributing to year-round supply and its potential application in urban and space agriculture.