Empowering multitrait brain phenotypes GWAS
Empowering multitrait brain phenotypes GWAS
Auvergne, A.; Traut, N.; Julienne, H.; Frouin, A.; Toro, R.; Aschard, h.
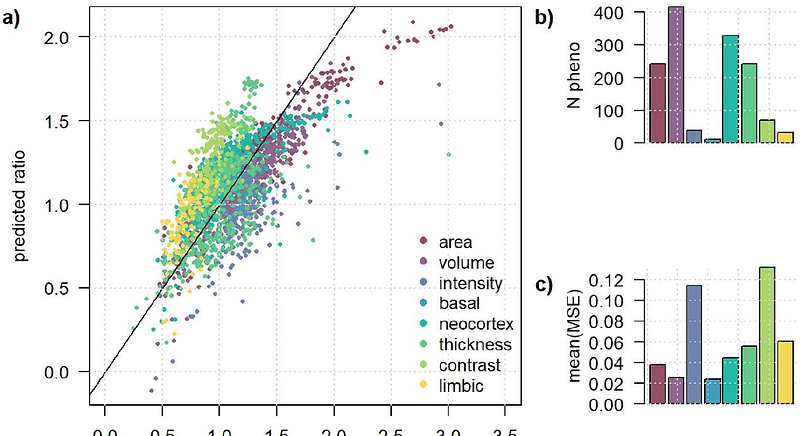
AbstractBrain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) data are now becoming available in human genetic cohorts including thousands of participants, providing a powerful mean to decipher the genetic architecture of brain phenotypes. Univariates genome-wide association screenings (GWAS) are typically applied as a baseline approach, but there are increasing interest for multitrait approaches to both increase statistical power and uncover shared structure underlying those phenotypes. However, there are limited guidelines on how to select phenotypes to be analyzed jointly and optimize power. Here we investigated factors impacting variant discoverability of state-of-the art multitrait GWAS using 1,010 MRI-derived phenotypes measured in 32,947 participants from the UK Biobank. Our study shows that the expected gain of multitrait approaches over univariate GWAS is highly predictable. We further propose data-driven strategy to define optimize sets and compare its performances with biologically driven approaches.