Simultaneous Sensing and Stimulation in Neuromodulation Systems: Quantifying and Mitigating Charge Accumulation Effects
Simultaneous Sensing and Stimulation in Neuromodulation Systems: Quantifying and Mitigating Charge Accumulation Effects
Orser, H.; Doan, P.
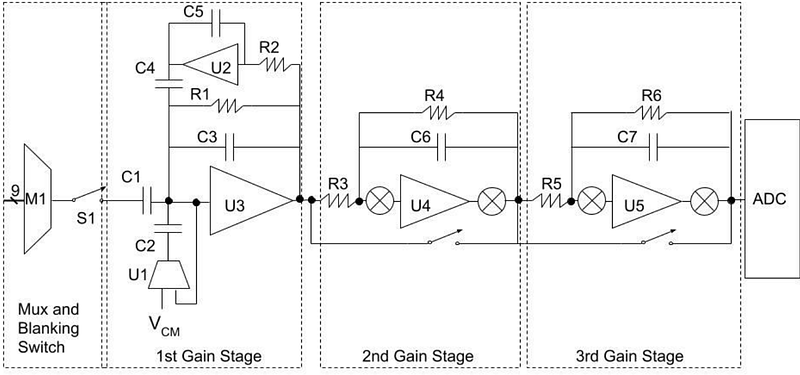
AbstractThis paper describes the operation of a low-noise amplifier and neurostimulation circuit when both functions are used simultaneously. The design of this circuitry along with the circuit model used to investigate system interactions is described. Expected circuit operation is explored in conjunction with the impact of charge storage at the electrode tissue interface. The test results for the system during independent use of the amplifier and during simultaneous use of the amplifier and stimulator are presented. As seen in the circuit analysis, test results confirm that the charge storage that occurs in the tissue/electrode interface used for stimulation interferes with the measurement of the neural signals of interest when the two circuits share electrodes. By optimizing the configuration used for the amplifier during high frequency stimulation, biological signals can be measured; however, the effective number of bits (ENOB) will be degraded as a function of the stimulation parameters, limiting the applications in which signal amplification can be meaningfully used when sharing an electrode with stimulation circuitry.