Structure-activity relationship of an all-α-helical prenyltransferase reveals a mechanism for indole prenylation.
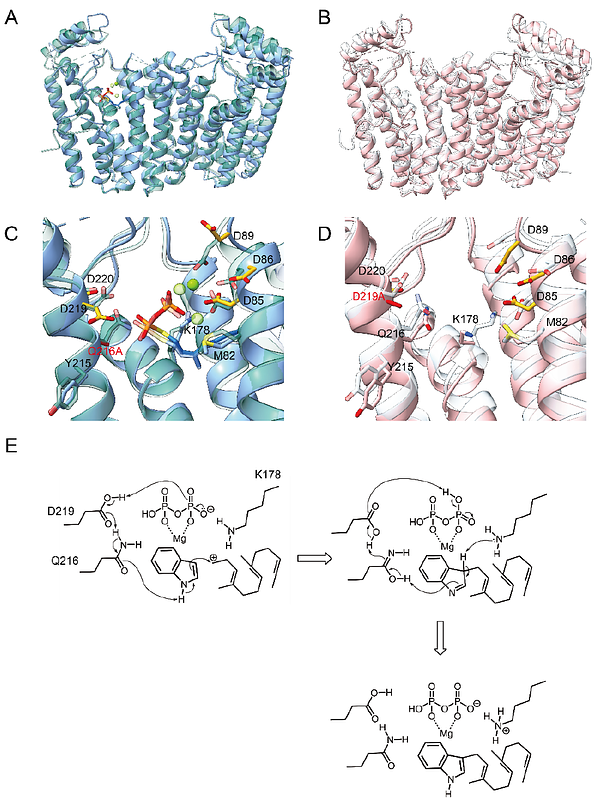
Structure-activity relationship of an all-α-helical prenyltransferase reveals a mechanism for indole prenylation.
Oshiro, T.; Uehara, S.; Tanaka, Y.; Ito, T.; Kodera, Y.; Matsui, T.
AbstractEnzymes are involved in the biosynthesis of various secondary metabolites found in nature. The catalytic mechanism is regulated by the three-dimensional structure of the enzyme especially at the catalytic site, resulting in the natural products with complicated conformation derived from a regioselective, chemoselective, and stereoselective fashion of the enzyme reaction. Prenyltransferase (PT), which belongs to the prenylsynthase (PS) family, catalyzes the condensation of isoprene to an aromatic compound, consequently producing a terpenoid scaffold structure. Therefore, it plays an important role in which expands the chemical diversity of terpenoids. Although the three-dimensional structures of PS which categorized in the same family were resolved, the catalytic mechanism of the PT has been vailed. In this study, we determined the X-ray crystal structure of a novel prenyltransferase SxPT1 derived from marine Streptomyces. Here we described that SxPT1 analyzed the enzyme reactions and discussed its catalytic mechanism.