Connecting afterglow light curves to the GRB central engine
Connecting afterglow light curves to the GRB central engine
Muhammed Diyaddin Ilhan, Kai Schwenzer
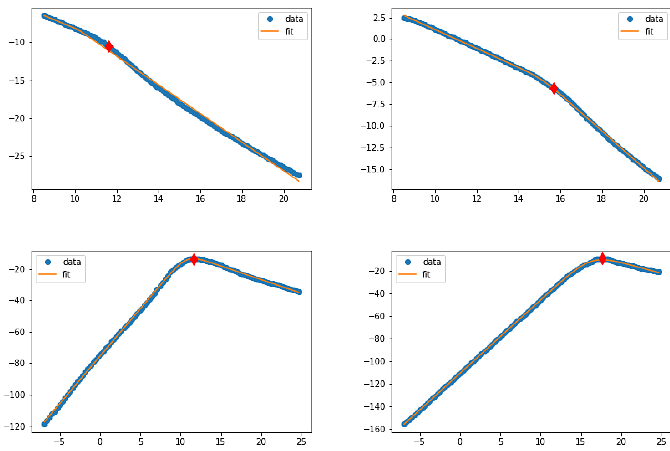
AbstractGamma ray burst (GRB) afterglow light curves have the potential to inform us about presently unobserved stages in the aftermath of a neutron star merger. Using numerical simulations of short GRB afterglows we obtain an approximate quantitative connection between key aspects of the emission mechanism and the shapes of the resulting light curves. Employing simple, but efficient, parameterizations of the light curve based on a broken power law in terms of physical parameters, fitted to a large dataset of synthetic light curves, we apply basic machine learning techniques to determine the approximate connection between key input parameters of the forward shock model and the light curve parameters. Solving then the inverse problem, we find that the strength of the central engine can be reasonably accurately estimated even with very limited information. In particular, merely the position of jet-break in the on-axis, respectively the maximum in the off-axis light curve determines the kinetic energy at the tens of percent level.